什麼是內臟脂肪?它為什麼危險?
內臟脂肪,顧名思義,是堆積在腹腔內臟器官周圍的脂肪。適量的內臟脂肪可以保護內臟,但過多的內臟脂肪就像一顆不定時炸彈,悄悄地危害我們的健康。
想像一下,你的內臟器官被一層厚厚的脂肪包裹著,它們的正常功能受到阻礙。過多的內臟脂肪會導致:
代謝異常
內臟脂肪會釋放大量的游離脂肪酸(FFA),干擾血糖和血脂的正常代謝。游離脂肪酸過多時會導致胰島素阻抗。
心血管疾病風險增加
與皮下脂肪不同,內臟脂肪會直接影響肝臟,導致膽固醇升高,增加動脈硬化的風險,從而提高心血管疾病的發生率。研究顯示,內臟脂肪是心血管疾病的獨立風險因子。
發炎反應
內臟脂肪會分泌發炎物質,長期下來可能引發慢性發炎,增加罹患糖尿病、癌症等疾病的風險。
其他疾病
研究顯示,內臟脂肪過高與第二型糖尿病、乳癌等疾病有密切關聯。
如何判斷內臟脂肪是否過高?
判斷內臟脂肪是否過高,不能只看體重。以下方法可以幫助你初步評估:
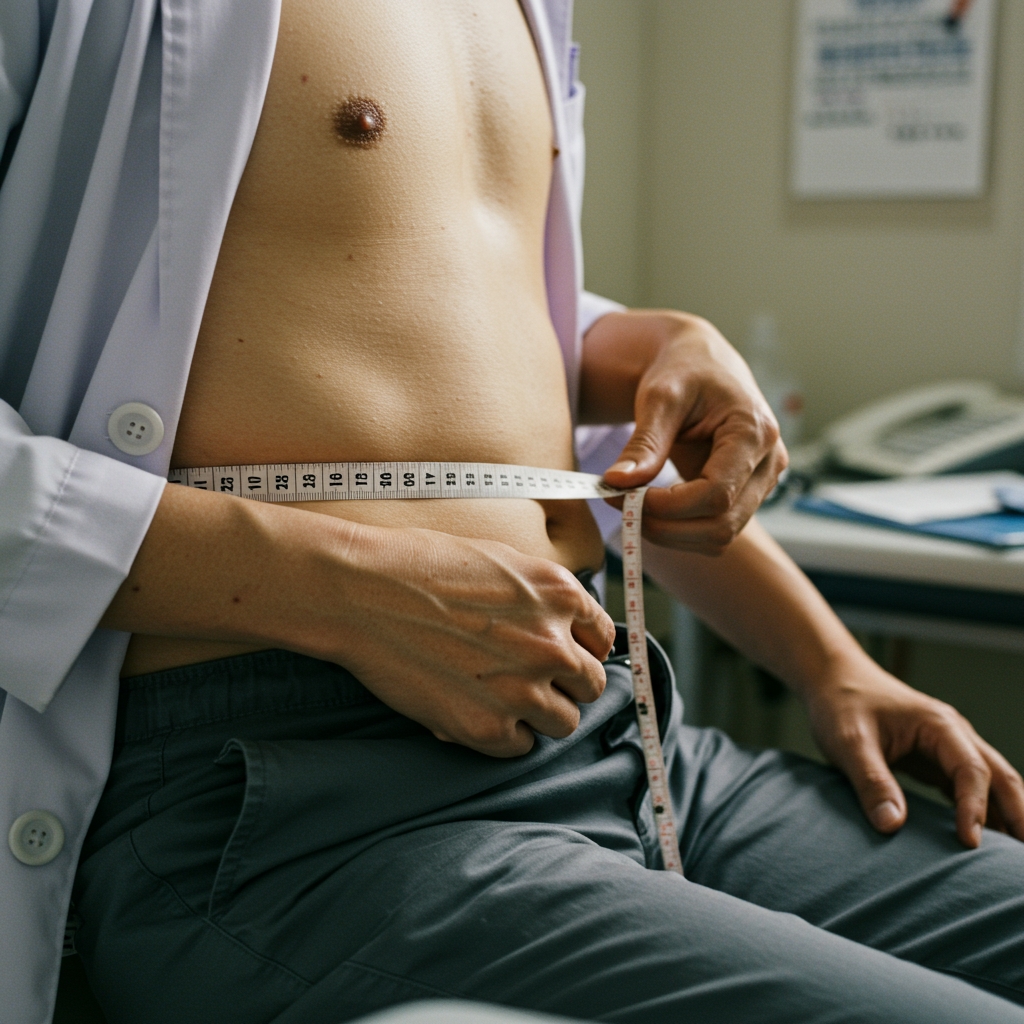
腰圍測量
這是最簡單直接的方法。男性腰圍超過90公分(約35吋),女性腰圍超過80公分(約31吋),就表示內臟脂肪可能超標。量腰圍時,應站直,將皮尺繞過肚臍上方,水平測量。
腰臀比
腰圍除以臀圍。男性腰臀比大於0.9,女性大於0.8,也可能表示內臟脂肪過高。
身體組成分析儀
透過生物電阻分析(BIA)測量體脂率和內臟脂肪指數。市面上許多體重計都具有這項功能。
專業醫療影像檢查
如電腦斷層掃描(CT)或核磁共振(MRI),可以精確測量內臟脂肪面積。不過,這些檢查通常費用較高,且具有輻射風險,不建議作為常規檢查。
如何有效減少內臟脂肪?
減少內臟脂肪並非難事,關鍵在於生活習慣的調整,以下分享推薦的生活習慣:
飲食控制
- 減少精緻澱粉和糖分的攝取:避免含糖飲料、甜點、油炸食物等高熱量、低營養價值的食物。
- 增加膳食纖維的攝取:多吃蔬菜、水果、全穀類,增加飽足感,有助於控制食慾。
- 選擇健康的脂肪:避免飽和脂肪和反式脂肪,選擇富含Omega-3脂肪酸的魚類、橄欖油、堅果等。
- 健康飲食:食用橄欖油、堅果、種子、豆類和全穀物。
規律運動
- 有氧運動:如跑步、游泳、騎自行車等,可以有效燃燒脂肪。建議每週至少進行150分鐘的中等強度有氧運動,或75分鐘的高強度有氧運動。
- 高強度間歇訓練(HIIT):研究顯示,高強度間歇訓練比傳統有氧運動更能有效減少內臟脂肪。
- 重量訓練:增加肌肉量,提高基礎代謝率,有助於長期控制體重和體脂。
作息規律
熬夜會影響內分泌,增加內臟脂肪堆積。保持充足的睡眠,有助於身體代謝和脂肪燃燒。
壓力管理
長期處於壓力下,身體會分泌壓力荷爾蒙,促進脂肪儲存。學習有效的壓力管理技巧,如冥想、瑜伽等,有助於減少內臟脂肪。
積極面對,與專業醫師攜手戰勝隱形肥胖
了解內臟脂肪的危害,並不可怕,反而能讓我們更積極地面對它。透過健康的生活方式,我們可以有效減少內臟脂肪,遠離疾病的威脅。
每個人的身體狀況不同,最好的方式是諮詢專業醫師或營養師,制定個人化的飲食和運動計畫。讓我們一起努力,戰勝隱形肥胖,擁抱健康的生活!
Reference
[1] Visceral Fat: Culprit or Canary? /Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America /2020 LINK
[2] Correlation of visceral body fat with waisthip ratio, waist circumference and body mass index in healthy adults: A cross sectional study. /Medical journal, Armed Forces India /2020 LINK
[3] Visceral and ectopic fat, atherosclerosis, and cardiometabolic disease: a position statement. /The lancet. Diabetes & endocrinology /2019 LINK
[4] Changes in body composition and metabolic disease risk. /European journal of clinical nutrition /2019 LINK
[5] Thakur KT, Boubour A, Saylor D, et. al.: Global HIV neurology: a comprehensive review. AIDS 2019; 33: pp. 163184.
[6] Rao G., PowellWiley T.M., Ancheta I., et. al.: Identification of obesity and cardiovascular risk in ethnically and racially diverse populations: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015; 132: pp. 457472.
[7] American Diabetes Association : 8. Obesity management for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes2020. Diabetes Care 2020; 43: pp. S89S97.
[8] Relationship of Visceral Fat and Adipokines with Cardiometabolic Diseases in Psoriasis. /Acta dermatovenereologica /2019 LINK
[9] Bray G.A., Fruhbeck G., Ryan D.H., et. al.: Management of obesity. Lancet 2016; 387: pp. 19471956.
[10] Timerestricted eating with or without lowcarbohydrate diet reduces visceral fat and improves metabolic syndrome: A randomized trial. /Cell reports. Medicine /2022 LINK
[11] Impact of highintensity interval training and sprint interval training on peripheral markers of glycemic control in metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. /Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular basis of disease /2020 LINK
[12] Impact of Intermittent Fasting Combined With HighIntensity Interval Training on Body Composition, Metabolic Biomarkers, and Physical Fitness in Women With Obesity. /Frontiers in nutrition /2022 LINK
[13] Impacts of lifestyle behavior and shift work on visceral fat accumulation and the presence of atherosclerosis in middleaged male workers. /Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension /2020 LINK
[14] Dietary habits affect fatty acid composition of visceral adipose tissue in subjects with colorectal cancer or obesity. /European journal of nutrition /2020 LINK
[15] Population Approaches Targeting Metabolic Syndrome Focusing on Japanese Trials. /Nutrients /2019 LINK
[16] Effect of HighIntensity Interval Training Combined with Blood Flow Restriction at Different Phases on Abdominal Visceral Fat among Obese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. /International journal of environmental research and public health /2022 LINK